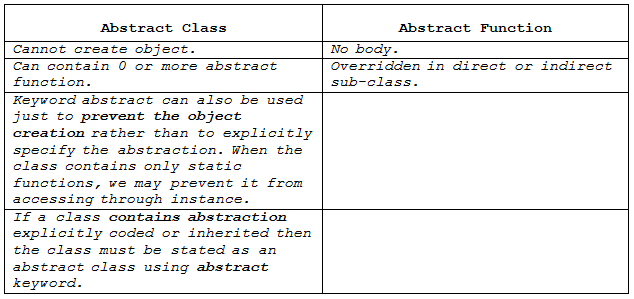
/** Abstraction refers to vague definition or not very definitive nature of a class or a method.
* An abstract function should not have a body.
* If a class contains abstraction explicitly coded or inherited then the class must be stated as
* an abstract class using abstract keyword.
* A class with at least one abstract method should be declared abstract.
* We cannot create objects of an abstract class.
* Abstraction is used to enforce specifications and to hide complexity.
* A class inheriting an abstract class should define (should give body by overriding them) all
* the abstract functions in it or should be explicitly declared abstract.
**/
abstract class Vehicle {
public abstract int numOfWheels();
public abstract String steeringType();
public abstract boolean hasGears();
public abstract String fuelType();
public abstract String getModel();
}
abstract class TwoWheelers extends Vehicle {
public int numOfWheels() {
return 2;
}
public String steeringType() {
return "Handle Bar";
}
}
abstract class FourWheelers extends Vehicle {
public int numOfWheels() {
return 4;
}
public String steeringType() {
return "Steering Wheel";
}
}
class Stallion extends TwoWheelers {
public boolean hasGears() {
return true;
}
public String fuelType() {
return "Aviation Fuel";
}
public String getModel() {
return "AK Automobiles - Stallion[NxtGen]";
}
}
class Turtle extends TwoWheelers {
public boolean hasGears() {
return false;
}
public String fuelType() {
return "Diesel";
}
public String getModel() {
return "AK Automobiles - Turtle[No Worries]";
}
}
class LoneRider extends FourWheelers {
public boolean hasGears() {
return true;
}
public String fuelType() {
return "Petrol";
}
public String getModel() {
return "AK Automobiles - LoneRider[Care For No One]";
}
}
abstract class RentAVehicle {
public static Vehicle getVehicle(String model) {
Vehicle vehicle = null;
if (model.equalsIgnoreCase("Stallion")) {
vehicle = new Stallion();
} else if (model.equalsIgnoreCase("Turtle")) {
vehicle = new Turtle();
} else if (model.equalsIgnoreCase("LoneRider")) {
vehicle = new LoneRider();
}
return vehicle;
}
}
class TestAbstraction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Vehicle vehicle = RentAVehicle.getVehicle(args[0]);
System.out.println(" Type: " + vehicle.numOfWheels() + " Wheeler");
System.out.println("Steering Type: " + vehicle.steeringType());
System.out.println(" Gear: " + (vehicle.hasGears() ? "Geared" : "Gearless"));
System.out.println(" Fuel Type: " + vehicle.fuelType());
System.out.println(" Model: " + vehicle.getModel());
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
System.out.println("Error in usage !!!");
System.out.println(getUsage());
} catch (NullPointerException ex) {
System.out.println("Sorry we do not have the specified model: " +
args[0]);
}
}
private static String getUsage() {
return "Usage: java TestAbstraction <\"vehicle name\">";
}
}
