—Rectangle.class—
public class Rectangle {
private int length = 0;
private int breadth = 0;
public Rectangle() {}
public Rectangle(int value) {
length = value;
breadth = value;
}
public Rectangle(int length, int breadth) {
this.length = length;
this.breadth = breadth;
}
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
public int getBreadth() {
return breadth;
}
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
public void setBreadth(int breadth) {
this.breadth = breadth;
}
public int calcArea() {
return length * breadth;
}
}
—TestRectangle.class—
class TestRectangle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
System.out.println("r1 Length: " + r1.getLength()); // 0
System.out.println("r1 Breadth: " + r1.getBreadth()); // 0
System.out.println("r1 Area: " + r1.calcArea()); // 0
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle(10);
System.out.println("r2 Length: " + r2.getLength()); // 10
System.out.println("r2 Breadth: " + r2.getBreadth()); // 10
System.out.println("r2 Area: " + r2.calcArea()); // 100
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
Rectangle r3 = new Rectangle(10, 20);
System.out.println("r3 Length: " + r3.getLength()); // 10
System.out.println("r3 Breadth: " + r3.getBreadth()); // 20
System.out.println("r3 Area: " + r3.calcArea()); // 200
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
r1.setLength(100);
r1.setBreadth(200);
System.out.println("r1 Length: " + r1.getLength()); // 100
System.out.println("r1 Breadth: " + r1.getBreadth()); // 200
System.out.println("r1 Area: " + r1.calcArea()); // 20000
}
}
—Container.class—
public class Container extends Rectangle {
private int height = 0;
public Container() {
super(0);
}
public Container(int value) {
super(value);
height = value;
}
public Container(int length, int breadth, int height) {
super(length, breadth);
this.height = height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public int calcVolume() {
return calcArea() * height;
}
}
—TestContainer.class—
class TestContainer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Container c1 = new Container();
System.out.println("c1.getLength(): " + c1.getLength()); //0
System.out.println("c1.getBreadth(): " + c1.getBreadth()); //0
System.out.println("c1.getHeight(): " + c1.getHeight()); //0
System.out.println("c1.calcArea(): " + c1.calcArea()); //0
System.out.println("c1.calcVolume(): " + c1.calcVolume()); //0
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
Container c2 = new Container(10);
System.out.println("c2.getLength(): " + c2.getLength()); //10
System.out.println("c2.getBreadth(): " + c2.getBreadth()); //10
System.out.println("c2.getHeight(): " + c2.getHeight()); //10
System.out.println("c2.calcArea(): " + c2.calcArea()); //100
System.out.println("c2.calcVolume(): " + c2.calcVolume()); //1000
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
Container c3 = new Container(10, 20, 30);
System.out.println("c3.getLength(): " + c3.getLength()); //10
System.out.println("c3.getBreadth(): " + c3.getBreadth()); //20
System.out.println("c3.getHeight(): " + c3.getHeight()); //30
System.out.println("c3.calcArea(): " + c3.calcArea()); //200
System.out.println("c3.calcVolume(): " + c3.calcVolume()); //6000
}
}
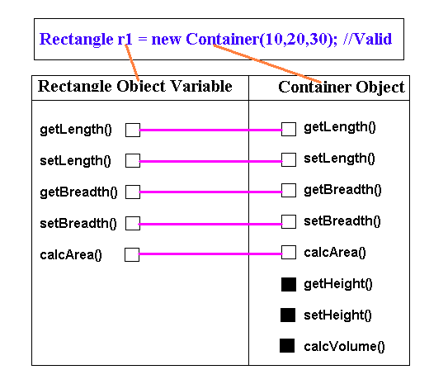
Rectangle r = new Container(10, 20, 30); /*valid because where ever a class (instance) is expected, we can pass its instance or the instance of its direct or indirect subclass*/
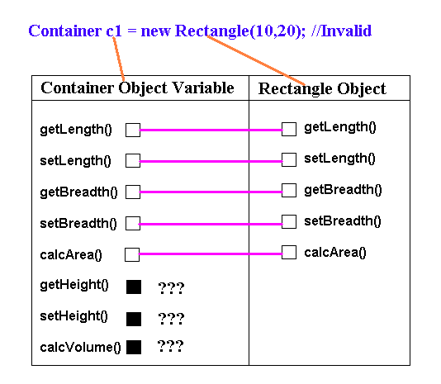
Container c = new Rectangle(10, 20); /*invalid because of the reason above; Here class Rectangle is the super class of class Container*/